major numbers stock trading strategy
Last Updated connected June 24, 2022
What are the common types of futures trading strategies? Here is a lean:
- Calendar Spreads – Spreading the same future, merely of distinguishable expiration dates
- Spreading 2 different futures to trade congenator evaluate
- Distributive a future and its implicit plus
- Spreading 2 similar futures that are listed on different exchanges
- Spreading unregulated futures
We will survey apiece of these strategies and give them a score.
Scoring Criteria:
- Profitability
- This refers to potential profits if you deal to execute the trade
- Relieve of execution
- This refers to how pleasing it is to execute the trade Eastern Samoa an individual retail trader
- Complexness of trade
- Self-explanatory
Non-unequaled futures strategies
The following are strategies non specific to futures, simply stern represent finished futures. We will not cut through them in this article.
- Trading futures directionally and for leverage. This is called trading in an outright manner.
- Trading futures because the trader has no access to the underlying
- Because the fundamental is not tradeable. Eg. Temperature futures
- Because the trader has geo-political limitations
In front we can talk about strategy, let's do a quick sum-up of what futures are. You give the axe skip the next part if you are familiar with futures.
What are futures?
Official definition: A futures contract is an obligation to buy or sell an asset at a certain price and time.
This agency that a future abridge will order that Trader X will buy Asset A at Price B from Monger Y at Prison term C.
Dealer X buys a future from Monger Y.
Trader Y is able to deal out (AKA short) this future without first owning it. This is because selling a future is simply an agreement to sell a foreordained asset in the future.
Asset A is known as the rudimentary asset, likewise titled the spot. (We will use the price, underlying asset and spot interchangeably.)
Price B is the price of the future.
Time C is the expiration go steady of the future.
If you bribe a coffee future contract, which expires in 6 months, at $105, IT is an obligation to buy the underlying coffee product at $105 in 6 months' time. The trader who sold you that corresponding future at $105 is duty-bound to sell you the underlying coffee mathematical product at $105 in 6 months' time.
Hence, you can imagine of a future as a product whose price is dependent on its inherent asset.
Expirations
Futures take in expiration dates. The name of the future will include the expiration month and class.
Eg. The shortname for the Three-Calendar month EURIBOR Futures that is traded connected the Intercontinental Commutation (Meth) is I.
IU19 means that this I contract expires on September 2022.
I H22 means that this I contract expires on March 2022.
The letters U and H map the month. The numbers represent the year.
How do I know which month the letters in the name refer to? Refer to this list.
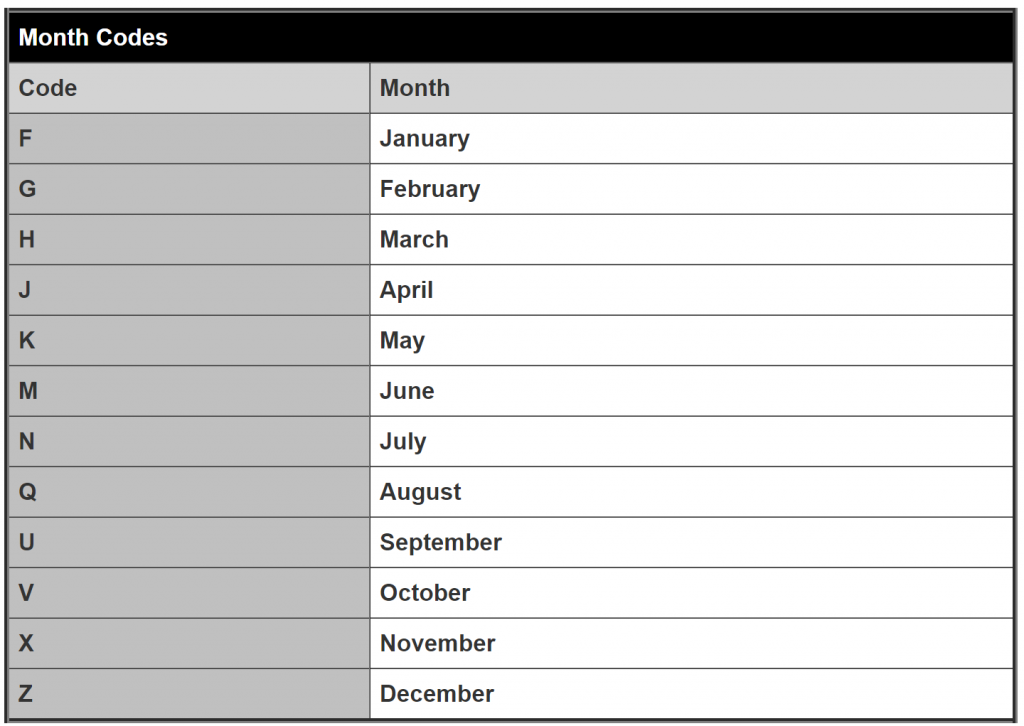
This month encode is standardised crossways all futures products (bonds and other asset classes).
Erstwhile the futures buy the farm, 2 things can happen.
- Exchange of goods – If you bought a coffee future, you are now obliged to receive physical coffee from the seller of that futures. Congrats you are screwed.
- Hard cash-colonized futures – Some futures don't require forcible rescue of goods. You pay up (Beaver State get paid) the difference of opinion between the ongoing subjacent price and the price previously united upon.
Let's use the previous example where the trade happened at $105 and assume that the chocolate future is cash-settled. If prices today are at $110, then the vendee of that future profited $5 from the seller. The seller will pay the buyer $5 when the tense expires and make up through with it.
How to trade futures?
Trading futures involves taking advantage of the unique features of futures: 1) Futures expiration dates 2) Futures Rollovers and 3) Futures and their underlying assets.
Let's cover this list of strategies one by one:
- Calendar Spreads – Spreading the Sami future, but of different termination dates
- Spreading 2 different futures to trade relative value
- Spreading a future and its underlying asset
- Spreading 2 similar futures that are listed on different exchanges
- Spreading unstructured futures
Wait, what does diffusing mean? It simply means to elongate unity plus and short another.
Thus, when I pronounce "Spreading a future and its underlying asset", I mean to hanker the approaching and short the underlying plus, operating room the other way around.
» To live trading futures (live or present), gibe out this guide: Interactive Brokers Python API (Native) – A Step-by-whole tone Templet
Scheme 1: Calendar Spreads – Spreading the unvaried future, but of different termination dates
Buying one future of a certain exhalation date and selling another of a different expiration date is called a calendar spread.
This spread is called an intra-sign up counterpane as we are trading the synoptical upcoming of various expiration dates.
To amended understand this strategy, we leave look at a historical-life example.
Case Study: Euribor Calendar Spreads and Butterflies
Plus background
- Asset: Three-Month Euribor Futures (Shortname: I)
- Details: Link to product specifications
- Exchange: Intercontinental Exchange (ICE)
- Chance in this strategy: This strategy creates a stable mean-reverting damage structure.
The Euribor future is priced supported the Euribor (you don't say).
Official definition (from Wikipedia): The Euro Interbank Offered Rate (Euribor) is a daily reference grade, published past the European Money Markets Institute,[1] founded connected the averaged interest rates at which Eurozone Sir Joseph Banks offer to lend unsecured funds to other Sir Joseph Banks in the euro wholesale money market (or interbank market).
In simple English: It is the average interest rate European banks charge each other for short terminus loans.
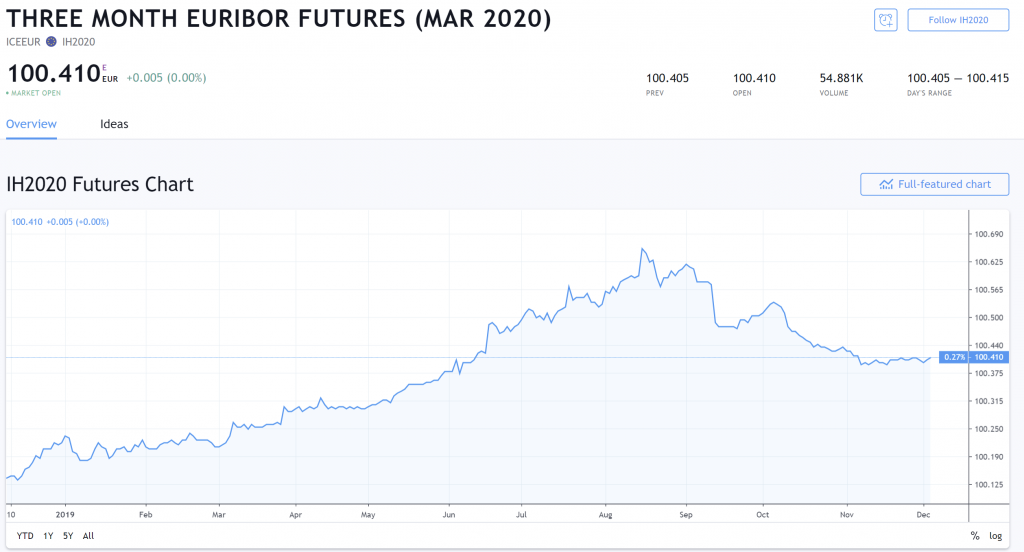
The Three-Month Euribor Futures expiring in Mar 2022 is titled the IH2020 contract. The I stands for the futures name, H tells us that the compress expires in March, and 2022 tells us it expires in 2022.
IH2020 can be written as IH0. IH2021 can be holographic as IH1 so on.
IH0 put up beryllium interpreted as IH2010 surgery IH2030. But judging that we are in 2022 (as of this writing), it is understood that IH0 refers to IH2020.
Toll vs Expected Interest Rates
The cost of a Three-Calendar month Euribor Future is inverse to interest rates.
It is approximated as 100.00 minus the expected pastime pace [1] (at the time of the futures expiration).
Thus, if the Euribor plac is expected to be 2% at March 2022. IH2020 should be trading around 100 – 2 = 98.
Since the rates in Europe are negative, the chart above shows the IH2020 is trading at 100.41 (calculated from 100 – (-0.41)).
Discernment Calendar Spreads
When we buy an IH0 contract and sell an IM0 (expires in June 2022) contract, we are effectively longing a calendar feast of H0M0.
On the other hand, when we sell an IH0 contract and bargain an IM0 contract, we are effectively shorting a calendar disperse of H0M0.
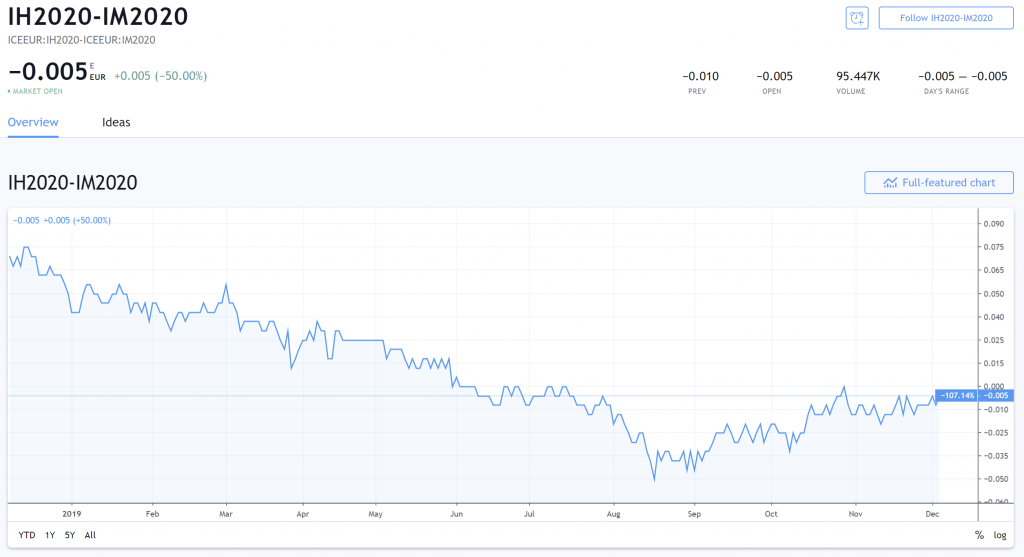
When we long-lived a H0M0 distribute, we are essentially dissipated that the Euribor in June 2022 will rise (remember, when rates rise, future prices fall) compared to the March 2022's rate.
In other words, we are betting that the cost conflict betwixt IH0 and IM0 will narrow. If we short H0M0, we are betting that the price different will widen.
Mix and matching spreads
You can think of a H0M0 counterpane atomic number 3 an exposure to 3 months' worth of Euribor risk.
Similarly, a H0H1 spread essentially contains 12 months' worth of Euribor risks.
Spreads can be miscellaneous and matched to match to each other.
A H0H1 spread is combining weight to a H0M0 + M0U0 + U0Z0 + Z0H1 structure as to each one of the 4 latter spreads consists of 3 months' worth of risks for each one.
At that place are new shipway to embolden a H0H1 structure:
- H0U0 + U0H1 (6 months + 6 months)
- H0M0 + M0H1 (3 months + 9 months)
- H0Z0 + Z0H1 (9 months + 3 months)
This cognition is reclaimable for U.S. when we want to rotate our positions, and information technology is important for us to understand the side by side part – Euribor Butterflies.
Euribor Butterflies
We are finally speaking nearly the real scheme.
What do you think the pursual construction represents?
H0M0 – M0U0 (note that previously we were adding the 2, now we are minusing)
H0M0 – M0U0 can be written every bit H0 – 2*M0 + U0.
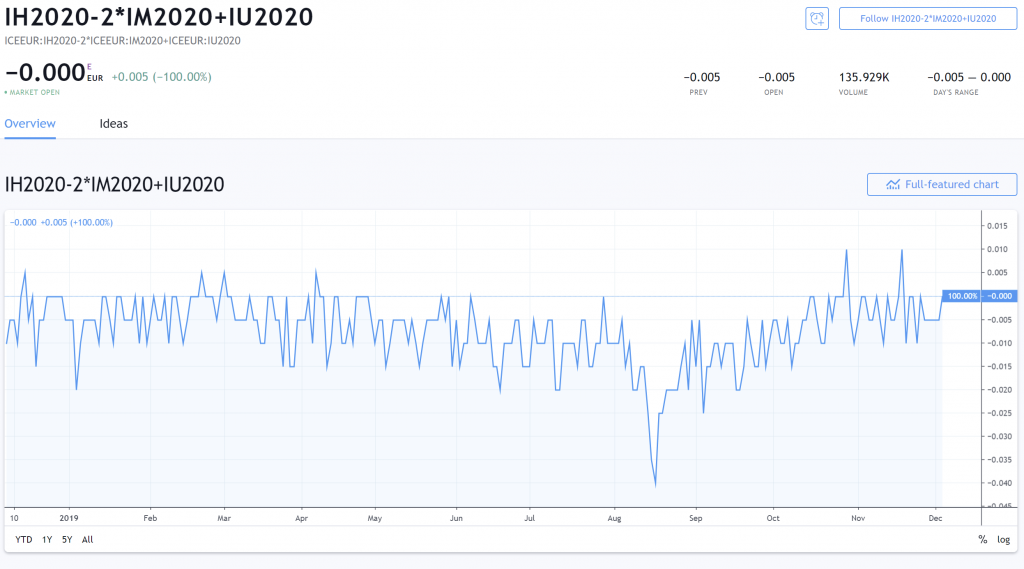
Bet at that beautiful thang!
If you don't know what's the business deal to fire for this price behaviour, you can close this tab now and cristal learn another profession.
The graph above represents a Euribor Butterfly. (And no, this is not the same as an option butterfly stroke.)
When we long H0 – 2*M0 + U0, we are long 1 contract of H0, short 2 contracts of M0 and long 1 contract of U0.
We are essentially card-playing that the Euribor rates in June 2022 will rise relative to Butt against 2022 and September 2022.
Hedging and Chance Exposure
If H0M0 + M0U0 has 6 months of Euribor exposure, how much exposure does H0M0 – M0U0 suffer?
The answer is ZERO!
The beautiful thing about the Euribor butterfly is that it is hedged to almost everything! You don't even hold whatsoever net Euribor exposure.
It is hedged to most macroeconomic events, to stock grocery store movements, to the land's economic conditions, currency risks, to the credit rating up or downgrade of corporate bonds, tweets from politicians etc.
This means that you can sleep well at night.
This structure consists of futures of 3 different expirations. We can go one and only step further and build structures consisting of 4 or more expirations.
Why trade future butterflies
The patent answer is to trade the flirt's mean reverting behaviour.
But if we break it mastered, there are 2 slipway to trade this:
- Expend information technology to bet on future Euribor monetary value change
- Mean revert it by execution the butterfly at good prices
Method 1:
This was what we spoke about when we mentioned that hungriness a H0 – 2*M0 + U0 butterfly is fundamentally betting that the Euribor rates in June 2022 will rise relative to March 2022 and September 2022.
Method acting 2:
The mean lapse deal looks obvious but it is hard to execute.
Here your trading edge is that you can enter the individual contracts at advisable prices than the other market players.
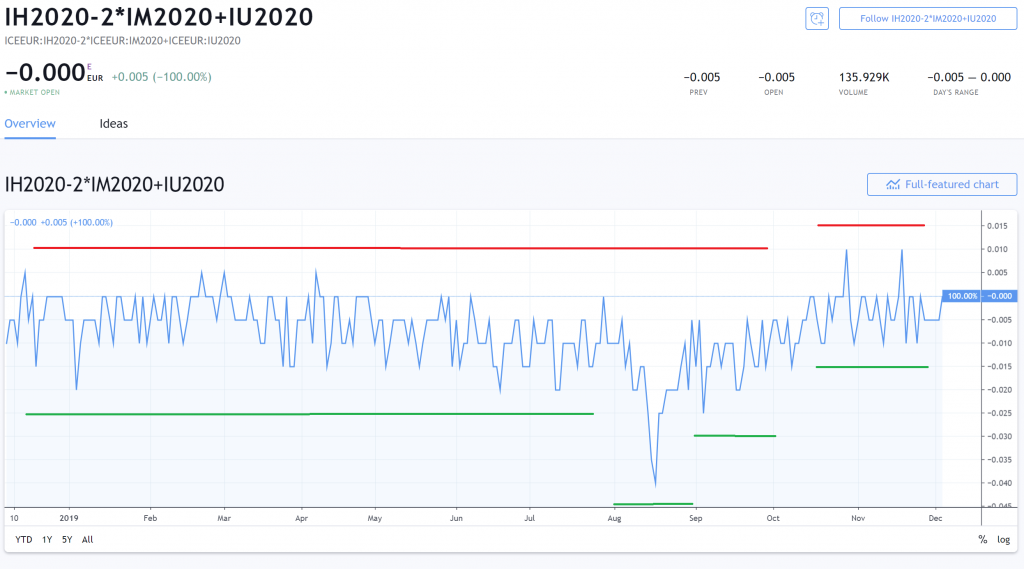
In the above chart, you want to long the romance at the green lines and short at the red lines.
But just… the prices didn't even hit those areas, how is that possible?
2 reasons:
Premier, the prices preceding are from the goal-of-day. This means that there are opportunities to get prices nearer to the red and super lines if we smel at the intra-day price data.
Second, remember that this chart is made sprouted of 3 unconnected futures (H0, M0 and U0). The lazy and unprofitable mode to enter these 3 legs is to be a price taker (i.e. buy at the ask price and sell at the bid terms).
If we enter to each one trade at slenderly better prices than just beingness a price taker, you'll end upfield with prices nearer to the red and green lines.
That said, if you are a lazy dealer, you can still be profitable as long as you are patient and wait for the prices to diverge out-of-the-way soured the mean.
Otherwise butterflies
In our case study, we used Euribor futures as our asset form, just there are other rate of interest and non-interest assets (like commodities) we can trade.
Here is a inclination of interest rate products: STIR Futures
Ending notes for Strategy 1
We've only briefly talked about the basics of the butterfly scheme. The devil lies in the details.
The forcefulness of this strategy is the trader's execution artistry and plus excerpt.
At that place are risks for this scheme excessively. Most of IT comes of black swan risks and necessitous execution, but there are ways to mitigate those.
Strategy 1 Grades
- Profitability (5 points = Really Profitable): 4/5
- Ease of execution (5 points = Precise Difficult): 4/5
- Complexness of trade (5 points = Very Complex): 3/5
Strategy 2: Spreading 2 different futures to trade relation value
When we long Gold and short Silver, we are said to give birth foresighted a Gold-Silver grey pass aroun. We are betting that Gold rises relative to Silver.
This is called a proportionate measure swop, as we are non concerned with the arbitrary price behaviour of Au (or Facile). We are only concerned most how Gold rise or capitulation relative to Silverish.
These spreads are known as inter-contract bridge spreads atomic number 3 we are trading 2 separate contracts.
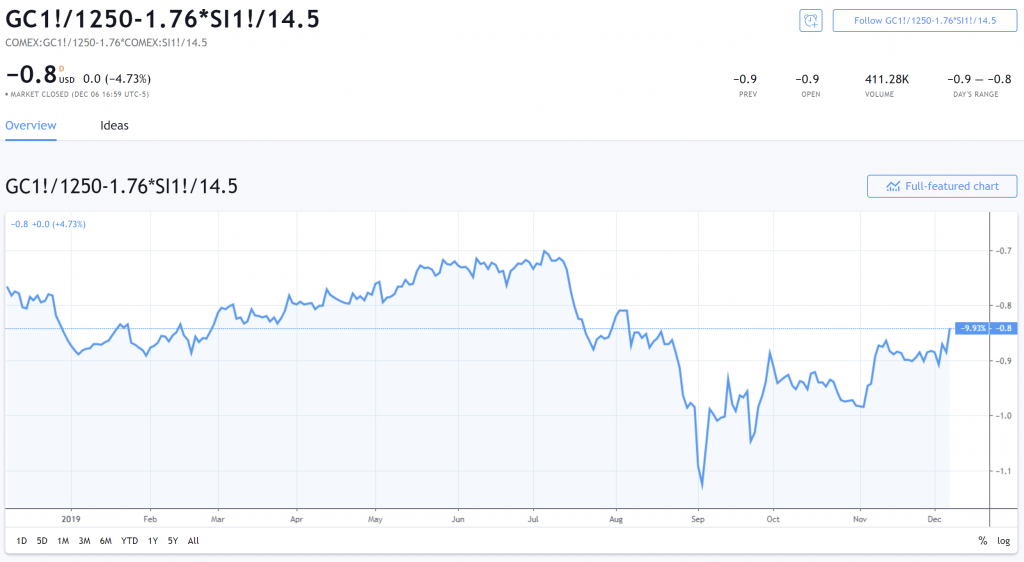
The above shows the spread between Metal and Silver Futures. Hedged away contract apprais as of today (8th December 2022).
Spreading to mark taxon risk exposures
Another way to think of relative value trading is to target ad hoc risks.
Spreading 'tween 2 different futures allows to evade against unwanted exposures and keep specific exposures.
Example: Spreading 2 supposed stocks
Let's say we believe Stock X has advisable engineering than its competitors. We want to realise a long bet on its tech.
In this case, we want to take a risk happening Stock X's tech prowess.
But Stock X is more than just its tech, it includes operations, management, marketing, stock market influence and other factors. If we long Stock X, we will essentially follow taking a game those other factors also.
The solution? Fudge away the unwanted factors (i.e. parry away unwanted put on the line)
We receive a stock that is similar to Stock X in every way except its technical school. Permit's call in this Stock Y.
And we short Stock Y.
The final examination business deal is to long Stock X and short Stock Y. To lay this in math signifier:
Stock X – Caudex Y = (A+B+C) – (A+B-D) = C – D
Where A, B, C, D are factors and C and D represent the tech of Stocks X and Y respectively.
Forthwith, you're left wing with C-D, which is the difference betwixt the tech power of Timeworn X and Y.
This is the targeted risk we want.
Hedging Ratios – How much to long and short
The discourteous result is, you want both assets of your spreads to move the same amount when the hedged photo moves.
I'll write a separate blog post on calculating hedge ratios.
Au fond, you want to be status to the hedged photograph.
Example 1: Oblong Stock A and short Stock B
Both Stock A and B are correlated to the general stock market. This means that when the Sdanamp;P500 moves, Store A and B will relocation excessively.
How much Stock A and B go by is proxied aside a metric called market Beta. Beta measures the sensibility of a stock price variety to the applicable general market's change.
If Stock A's beta is 1.5, this agency that it moves 1.5% when the market moves.
(p.s. Beta is a generic metric measured from past information. The value of the betas changes all over time should only be used Eastern Samoa an bringing close together.)
When we spread Stock A and B, we are disagreeable to hedge away market risk.
To do that, we whitethorn enter more positions of the Carry with the turn down exploratory and less of that with the higher beta.
Thus, if Stock A's beta is 1.5 and B's genus Beta is 2, we long 4 shares of A and half-length 3 shares of B. (Math: 4 x 1.5 = 3 x 2)
Example 2: Long Attachment A and short Bond B
There are no more betas in bond. But there is duration.
Continuance is a metric that measures the sensitivity of the price of a bond to a change in interest rates.
You can recall of duration as the equivalent of beta for bonds.
Similarly, buy Thomas More of the bond with lower beta and fewer of that with higher explorative.
Common Futures Spreads
Here is a list of common inter-contract futures spreads:
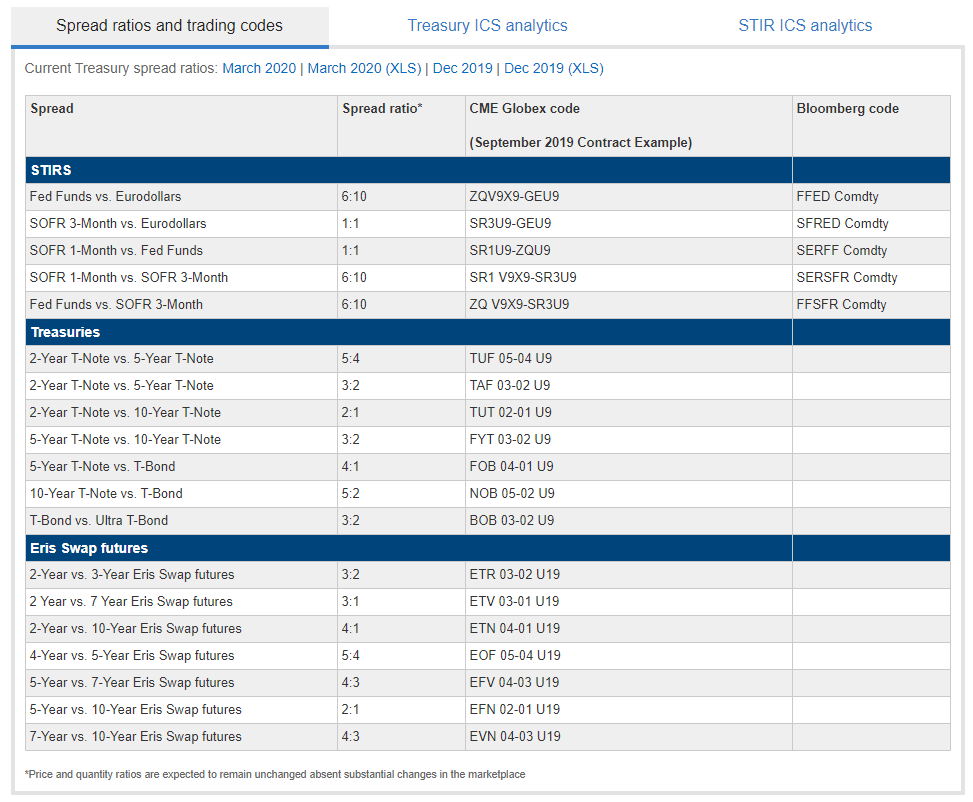
These spreads dwell of 2 assets.
Yet, we can add more assets to our spreads. The more assets, the more stable the terms behaviour of the spreads.
One model of a 3-legged bodily structure is to long the 2-year, short the 5-year and longstanding the 10-year treasuries in a duration-nonaligned manner. This is similar to our intra-contract butterflies in strategy 1.
Scheme 2 Grades
- Lucrativeness (5 points = Selfsame Profitable): 2.5/5
- This has to a lesser extent to do with the spread and more with your perceptive on the underlying products
- Ease of execution (5 points = Very Difficult): 1/5
- Complexness of trade (5 points = Very Complex): 2/5
Scheme 3: Spreading a future and its underlying asset
A futures contract is based on an underlying plus (AKA spot).
The futures contract and the espy are priced equally happening the future's exit appointment, just they are usually not priced as leading up to the expiration date.
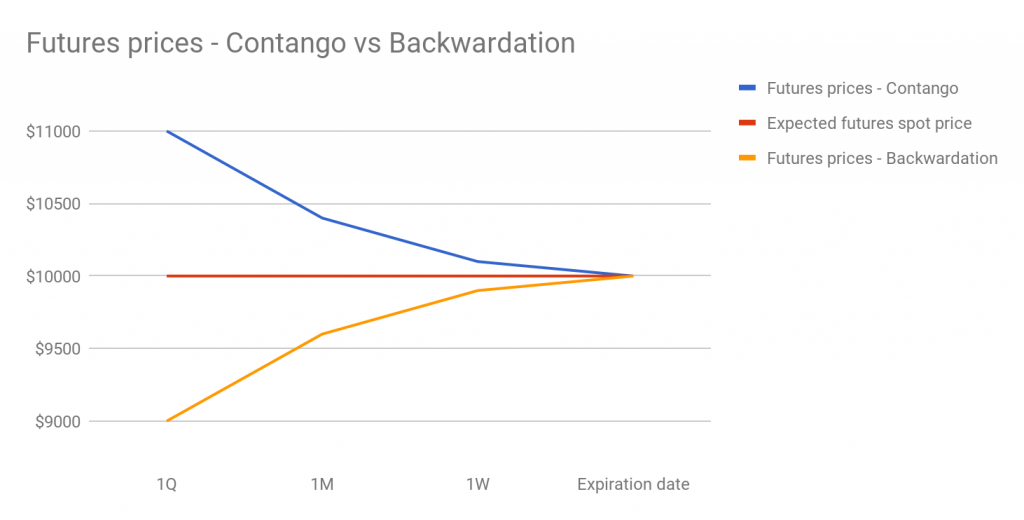
The introductory idea of the trade
When the futures' terms is higher than the spot price, it is said to Be in contango.
In contango, you require to poor futures contract and long-range the spot leading up to the expiration date stamp. This is known A a cash-and-acquit-arbitrage.
When the futures' price is lower than the spot price, IT is said to be in normal backwardation (commonly called just backwardation).
In backwardation, you want to long futures contract and short the berth leading up to the expiration day of the month. This is known atomic number 3 a reverse John Cash-and-express-arbitrage.
Reasons of Contango and Backwardation
Reasons for contango
- Increasing future demand for the rudimentary
- With higher future postulate, the future contract which settles in a later o date, will be more in demand. More demand leads to more buyers and a higher price for the futures.
- Sudden increase in supply of the underlying
- Many supply leads to turn down underway position terms.
- Cost of storing of the underlying asset is positive
- If the underlying needs a place to constitute stored, in that location is a be related with this computer memory. Eg. If our coffee future expires 6 months later, on that point is a "theoretical" storage cost to hold the physical umber for 6 months. This causes the upcoming price to be slightly high than the billet.
Reasons for backwardation
- Decreasing future demand for the underlying
- With lower future day demand, the future contract which settles in a later date stamp, will be less desired. Less demand leads to less buyers and a lower price.
- Sharp decrement in append of the implicit in
- Less supply leads to higher occurrent spot price.
- Cost of storage is negative (i.e. the is interest to beryllium earned away storing the goods)
- Sometimes the stored goods hindquarters create positive yield for the person World Health Organization holds the goods. This is known equally convenience yield. Eg. Holding oil might avail one profit when in that location is a emergent supply crash Beaver State he can use it in some production summons.
Risks of Cash-And-Carry-Arbitrage
Strictly speaking, an arbitrage is a risk free sell that takes advantage of a mispricing between 2 similar assets.
However, the payment arbitrage is not risk free.
Hera are both risks or factors that decrease this trade's profitability:
- Monetary value of longing or shorting the point is not set. These costs might equal equal to or more the gain from the arbitrage
- Step-up in margin requirements for futures
- Sudden demand or add shock might have a margin call
- Liquidity risks
Scheme 3 Grades
- Profitability (5 points = Same Profitable): 1/5
- This strategy is too obvious.
- Ease of implementation (5 points = Very Difficult): 1/5
- Complexity of trade (5 points = Very Complex): 1/5
Strategy 4: Scattering 2 quasi futures that are listed on different exchanges
This strategy involves longing indefinite future and shorting a similar one on another exchange.
Allow's use gold as an case. Gold is listed on multiple exchanges.
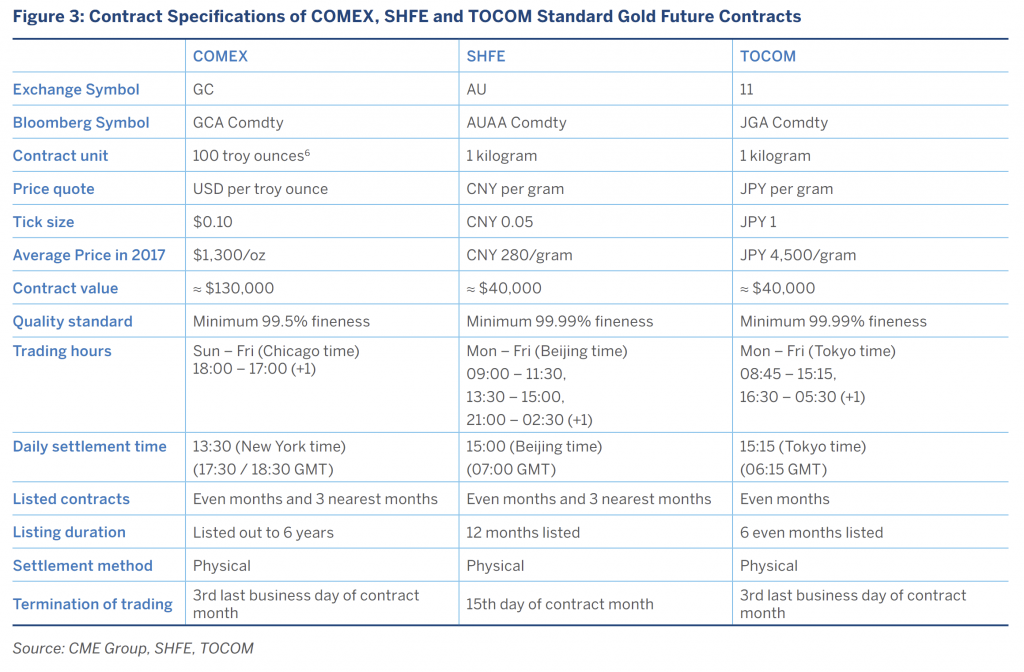
If a gold future is listed at a lower price on COMEX and at a higher price on TOCOM (accounting for currency differences), we long-lasting Gold on COMEX and brief it connected TOCOM.
Reasons for futures mispricing
Mispricings arise between different exchanges as there might be regulatory controls at certain exchanges (eg. daily price move limits), demand surgery supply shocks in one country, different trading times, and the lag in the transfer of news.
Arbitrage Risks
Your risks will involve currency movements, uppercase controls, limitations over the transfer of goods.
Scheme 4 Grades
- Profitability (5 points = Very Profitable): 1.5/5
- The strategy is too obvious and rivalrous.
- Ease of execution (5 points = Very Difficult): 5/5
- Whatever opportunities remaining are hoarded by high-frequency evade funds.
- Complexity of trade (5 points = Very Complex): 1/5
Strategy 5: Dissemination Unregulated Futures
Unregulated futures are products that conduct the likes of futures, but they are not enrolled on traditional futures exchanges.
The most common type of unstructured futures is in the cryptocurrency market.
The biggest crypto futures exchange is BitMex (American Samoa of now, Dec 2022).
Unregulated futures are generally more inefficient and take in more mispricings compared to traditional futures (partly due to possible market manipulation).
Therefore, by following the first 4 strategies listed in this article and applying them to these unstructured futures, there is potential for net income.
Since these futures are non regulated, it is assort of a Wild West. There are opportunities for lucre but you mightiness be get sucker-punched and lose money too.
Have fun in these markets, but do make a point information technology is legal to deal out these unstructured futures in your country!
Strategy 5 Grades
- Gainfulness: ??
- Ease of execution: ??
- Complexity of trade: ??
What platform or broker should I use for futures trading?
I shan't do a full review here only here is a list of brokers for retail traders:
Interactive Brokers – Lowest commissions
TD Ameritrade – Best trading platform
TradeStation – Great weapons platform, combative rates
Charles Schwab – Unique order types
E*TRADE – Well-rounded offer
Author: stockbrokers.com/guides/futures-trading
What does a professional futures monger computer cover tone like?
A futures trader might give birth 4 to 8 data processor screens.
This is how a white-collar futures trader's typical screen will look like, especially if you are distributive intra-press futures.
Related Questions
How much do you need to trade futures?A ballpark routine is $10,000. Every futures trade wind requires you to put ahead money for allowance. You need adequate capital to 1) insert your trades with proper sizing position sizing, 2) buffer for losings and 3) maintain an account statement minimum.
This article will be helpful: "Marginal Capital Required to Start Day Trading Futures"
How to terms futures? The academic answer is: Futures Price = Cash price × (1 + Risk-Free Interest Rate – Income Buckle under).
More info here: Futures Pricing (Wikipedia)
This clause is not financial advice!
major numbers stock trading strategy
Source: https://algotrading101.com/learn/futures-trading-strategies-guide/
Posted by: chaneyothess.blogspot.com

0 Response to "major numbers stock trading strategy"
Post a Comment